The Importance of Regular Diagnostic Checkups for Senior Citizens
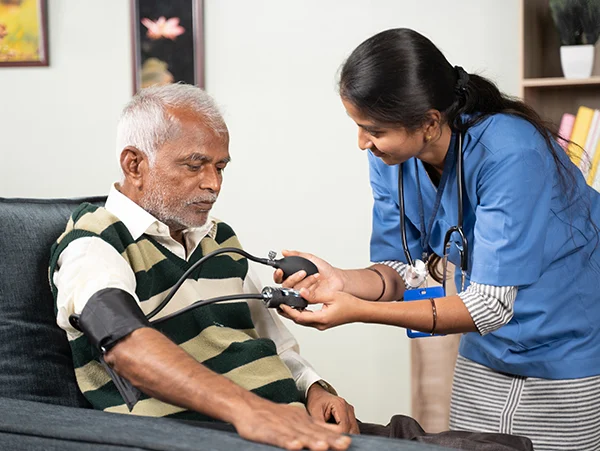
As we age, our bodies undergo various changes that can impact our health and well-being. For senior citizens, regular diagnostic checkups become increasingly vital to ensure that any potential health issues are identified and managed early. These checkups are crucial in maintaining a high quality of life, promoting longevity, and preventing serious health complications.
Why Regular Checkups Matter
1.Early Detection of Health Issues
Early detection is key to effectively managing many health conditions. Regular checkups can help identify issues such as hypertension, diabetes, heart disease, and cancer at an early stage when they are more treatable. This proactive approach can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
2.Monitoring Chronic Conditions
Many seniors live with chronic conditions that require ongoing management, such as arthritis, COPD, or osteoporosis. Regular checkups allow healthcare providers to monitor these conditions, adjust treatments as needed, and provide advice on lifestyle changes to help manage symptoms and improve overall health.
3.Medication Management
As people age, they often require multiple medications to manage various health conditions. Regular checkups provide an opportunity for doctors to review all medications, ensuring they are still necessary and effective, and to check for potential drug interactions that could cause adverse effects.
4.Preventive Care
Preventive care is a cornerstone of health maintenance for seniors. Routine screenings, vaccinations, and lifestyle counseling are essential components of a comprehensive checkup. Preventive measures can help avoid illnesses such as influenza, pneumonia, and shingles, which can be particularly severe in older adults.
Components of a Senior Citizen Diagnostic Checkup
1.Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination is the foundation of any diagnostic checkup. This includes checking vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate, temperature), assessing physical function and mobility, and examining the heart, lungs, abdomen, and other key areas.
2.Blood Tests
Blood tests can reveal a wealth of information about a senior’s health. Common tests include complete blood count (CBC), lipid profile, blood glucose levels, and liver and kidney function tests. These tests help identify issues such as anemia, high cholesterol, diabetes, and organ dysfunction.
3.Imaging Studies
Depending on individual risk factors and symptoms, imaging studies such as X-rays, ultrasounds, or MRIs may be recommended. These tests can help diagnose conditions like osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, or cancers.
4.Hearing and Vision Tests
Hearing and vision tend to decline with age, and regular testing is essential to maintain quality of life. Early detection of issues can lead to timely interventions such as hearing aids or corrective lenses.
5.Mental Health Evaluation
Mental health is just as important as physical health, particularly for seniors who may be at higher risk for conditions such as depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline. A mental health evaluation can help identify these issues early and provide access to appropriate treatments and support.
Tips for Seniors to Prepare for a Checkup
1.Keep a Health Journal
Keeping a journal of any symptoms, medications, and significant health events can help provide a clear picture of your health status to your healthcare provider.
2.List of Medications
Bring a list of all medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. This helps in managing potential drug interactions and ensuring optimal medication management.
3.Questions and Concerns
Write down any questions or concerns you have about your health. This ensures that you don’t forget to discuss important topics during your appointment.
4.Medical History
Be prepared to discuss your medical history, including any surgeries, hospitalizations, or chronic conditions. This information is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Conclusion
Regular diagnostic checkups are a critical component of maintaining health and well-being for senior citizens. By prioritizing these checkups, seniors can enjoy a better quality of life, manage chronic conditions effectively, and take proactive steps in preventing serious health issues. Encouraging and facilitating regular checkups for the elderly can make a significant difference in their overall health and longevity.